Dec. 24, 2025
As the global solar industry continues to scale, safety and compliance have become central topics for manufacturers, developers, and investors. Among all core materials, photovoltaic glass plays a decisive role in ensuring the durability, reliability, and long-term safety of solar modules. Understanding what safety standards photovoltaic glass must meet is therefore essential for anyone involved in the photovoltaic value chain.
Photovoltaic glass must comply with a comprehensive set of international standards for photovoltaics, building, fire protection, and electrical safety. These include the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards sy stem—IEC 61215 and IEC 61730; building-related standards; mechanical safety standards—EN 12150 and EN 1863; and fire resistance standards such as UL 1703, UL 61730, or IEC fire rating tests.
Photovoltaic glass is not merely a protective cover; it is a structural and functional component of solar modules. High-quality photovoltaic glass must withstand mechanical loads, extreme weather conditions, and long-term environmental exposure while maintaining optical performance. Any failure in photovoltaic glass can directly compromise module safety, energy yield, and project lifespan.
Because of this critical role, pv glass is subject to a wide range of international safety standards that regulate strength, impact resistance, fire performance, and electrical insulation.
Globally, photovoltaic glass must comply with several internationally recognized standards before it can be used in certified solar modules.
One of the most important frameworks is the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standard system. IEC 61215 and IEC 61730 define performance and safety requirements for photovoltaic modules, and photovoltaic glass is a key material evaluated during testing. These standards assess whether photovoltaic glass can endure thermal cycling, humidity freeze tests, and mechanical stress without cracking or delamination.
In parallel, pv glass used in building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) must also comply with construction-related standards, adding another layer of safety requirements.
Mechanical safety is one of the core evaluation criteria for photovoltaic glass. Tempered photovoltaic glass is widely used because it offers significantly higher strength compared to ordinary float glass. According to international standards, pv glass must pass load tests simulating wind pressure, snow load, and hail impact.
Standards such as EN 12150 and EN 1863 are often applied to tempered photovoltaic glass, ensuring that, in the event of breakage, the glass shatters into small, blunt fragments rather than sharp shards. This characteristic is critical for reducing injury risks and improving overall system safety.
Fire performance is another major safety concern. Photovoltaic glass must meet fire resistance and flame spread requirements, especially for rooftop and façade installations. Depending on the market, pv glass may need to comply with standards such as UL 1703, UL 61730, or IEC fire classification tests.
In many regions, photovoltaic glass used in BIPV systems must achieve specific fire ratings similar to architectural glass. This ensures that photovoltaic glass does not contribute to fire propagation and remains stable under high temperatures.
Although photovoltaic glass is not conductive, it plays a vital role in electrical insulation. Safety standards require pv glass to maintain high insulation resistance even in humid or polluted environments. During IEC and UL testing, photovoltaic glass is evaluated as part of the complete module to ensure no electrical leakage or insulation failure occurs over time.
This aspect is especially important for utility-scale projects, where photovoltaic glass must guarantee long-term operational safety under continuous high-voltage conditions.
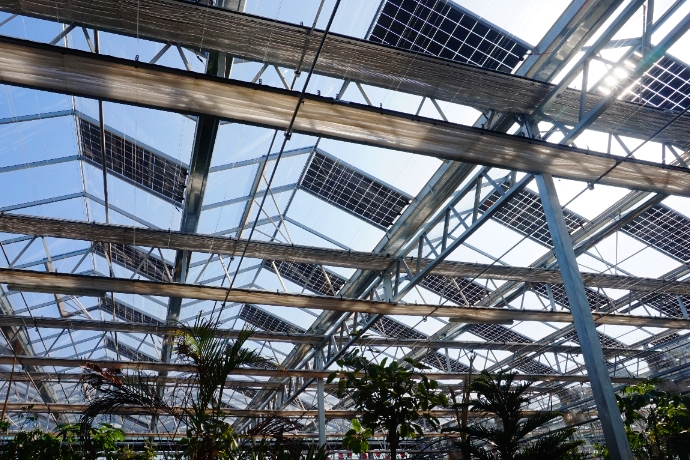

With the rapid growth of BIPV, photovoltaic glass increasingly functions as both an energy-generating material and a building envelope component. In these applications, photovoltaic glass must comply with building codes in addition to photovoltaic standards.
Laminated photovoltaic glass is commonly used in façades, skylights, and curtain walls to meet safety glass regulations. Standards such as EN 14449 and ANSI Z97.1 ensure that laminated pv glass remains intact after breakage, preventing falling debris and enhancing occupant safety.
Different markets impose additional certification requirements on photovoltaic glass. In the United States, compliance with UL standards is mandatory, while in Europe, CE marking and EN standards apply. In Asia-Pacific markets, photovoltaic glass often needs to meet both IEC standards and local regulatory requirements.
For manufacturers, ensuring that photovoltaic glass meets multi-regional safety standards is essential for global market access and project bankability.
As photovoltaic installations expand into urban environments, floating solar systems, and extreme climates, safety expectations for photovoltaic glass continue to rise. The industry is seeing increased demand for thicker, double-glazed, and coated pv glass solutions that offer enhanced strength and safety margins.
At the same time, insurers and financial institutions are placing greater emphasis on certified photovoltaic glass, recognizing its importance in minimizing operational risk and long-term maintenance costs.
So, what safety standards does photovoltaic glass meet? In practice, photovoltaic glass must comply with a comprehensive set of international photovoltaic, construction, fire, and electrical safety standards. From IEC and UL certifications to building safety regulations, photovoltaic glass is rigorously tested to ensure mechanical strength, fire resistance, electrical insulation, and long-term reliability.
As solar technology continues to evolve, photovoltaic glass will remain at the center of module safety and system performance. For developers, EPCs, and end users alike, choosing certified photovoltaic glass is not just a compliance issue—it is a critical investment in safety, durability, and sustainable energy infrastructure.